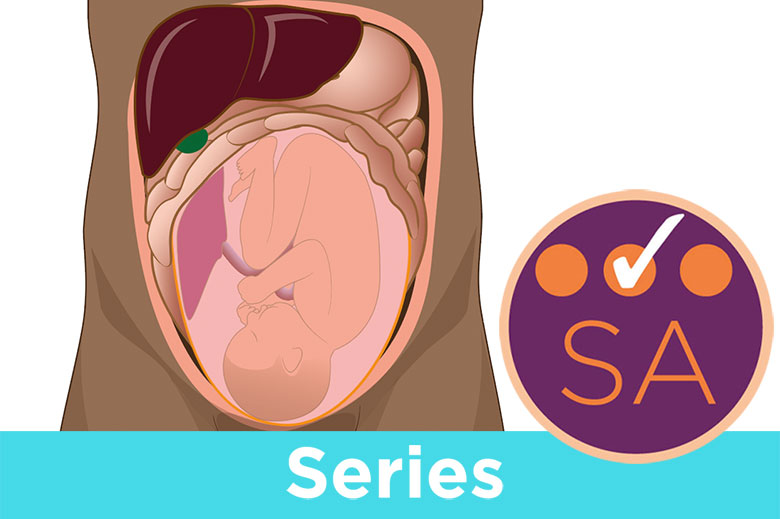
Maternal thyroid hormones build fetal neural pathways before the fetus develops its own gland. Undetected hypothyroidism raises miscarriage risks by 60%. Autoimmune thyroiditis silently disrupts placental nutrient transfer, starving fetal growth. Monthly TSH monitoring ensures levels stay below 2.5 mIU/L to prevent cognitive delays. Silent imbalances often evade standard prenatal screenings.
Insulin resistance rises naturally—but too much causes damage
Placental hormones spike glucose to prioritize fetal energy needs. Overworked maternal pancreases fail 1 in 7 pregnancies, triggering gestational diabetes. Post-meal glucose above 140 mg/dL thickens placental walls, reducing oxygen flow. Continuous glucose monitors reveal erratic spikes fingerstick tests miss. Unmanaged levels seed childhood obesity and metabolic disorders.
Cortisol increases—and not always in balance
Stress hormones double by the third trimester to mature fetal lungs. Chronic anxiety floods the placenta with excess cortisol, altering fetal stress responses. Saliva tests track nocturnal spikes linked to preterm labor risks. Mindful breathing practices lower cortisol by 18% within weeks. Silent stress reshapes fetal brain development.
Progesterone softens the body—but sometimes too much
This hormone relaxes uterine muscles to prevent premature contractions. Excess slows digestion, causing reflux and chronic constipation. Vaginal progesterone supplements reduce preterm labor risk by 45% in high-risk groups. Mood swings signal the need for dosage adjustments. Over-supplementation blunts emotional resilience.
Estrogen thickens tissue and blood—but when imbalanced, creates risk
Estrogen surges drive uterine expansion and breast duct development. Hyperestrogenism triples thrombosis risk by spiking clotting factors like fibrinogen. D-dimer tests after 20 weeks catch silent coagulation shifts. PCOS patients face amplified hypertension dangers due to preexisting estrogen dominance.
Prolactin starts preparing even before delivery
Milk-building hormones rise 20x during pregnancy, priming lactation months early. Excess prolactin flattens dopamine, numbing emotions in 12% of mothers. Cognitive behavioral therapy eases symptoms without risky medications. Postpartum prolactin rhythms sync with feeding cycles. Disrupted sleep prolongs depressive episodes.
DHEA helps maintain pregnancy—but too much can disrupt it
Fetal adrenal glands pump DHEA to fuel placental estrogen synthesis. Levels above 8 μmol/L trigger androgenization in PCOS patients, causing acne and hair loss. Supplements compete with progesterone, risking uterine irritability. Natural production suffices in most pregnancies.
Endocrine monitoring isn’t extra—it’s essential
First-trimester HbA1c predicts gestational diabetes better than BMI alone. Mid-pregnancy 24-hour urine cortisol tests expose hidden Cushing’s syndrome mimics. Third-trimester TSH fluctuations hint at postpartum thyroiditis risks. Standard panels miss 30% of subclinical endocrine disruptions.
The endocrine system co-parents the pregnancy
Hormones draft the pregnancy’s narrative—thyroid sets pacing, insulin drives conflict. Silent imbalances like subclinical hypothyroidism rewrite outcomes without warning. Labs decode hormonal whispers before they escalate. Care hinges on chemistry, not just ultrasound images.
Silent thyroiditis often mimics “normal” pregnancy fatigue
Undiagnosed thyroid inflammation masquerades as typical exhaustion. Antibody tests (TPO, TgAb) catch autoimmune attacks standard TSH screenings miss. Untreated cases correlate with preterm birth and low birth weight. Fatigue lasting beyond week 20 warrants deeper investigation.
Placental hormones hijack maternal metabolic balance
hPL and CRH force insulin resistance to prioritize fetal glucose. Maternal beta cells strain to compensate, often failing by mid-pregnancy. Early insulin therapy preserves pancreatic function and reduces NICU admissions.
Androgen imbalances seed complications in PCOS pregnancies
Elevated testosterone increases gestational diabetes risk fourfold in PCOS patients. Metformin use during pregnancy lowers miscarriage rates by 50% in this group. Postpartum androgen rebounds trigger hair loss and acne flare-ups.
Vitamin D deficiency amplifies endocrine risks
Low vitamin D (<30 ng/mL) worsens insulin resistance and thyroid dysfunction. Supplementation reduces preeclampsia risk by 25% in deficient mothers. Prenatal vitamins often underestimate optimal dosages for high-risk groups.
Postpartum thyroiditis flies under the radar
Up to 8% of women develop thyroid inflammation within a year of delivery. Symptoms like fatigue and weight gain mimic postpartum depression. TSH and antibody testing at 6 weeks postpartum prevent long-term dysfunction.
Cortisol’s dual role complicates stress management
While essential for fetal lung maturation, excess cortisol restricts placental blood flow. Nighttime salivary tests differentiate adaptive surges from pathological stress. Guided meditation lowers maternal cortisol by 22% in 30 days.
Oxytocin’s role extends beyond labor induction
This hormone strengthens uterine contractions and fosters maternal-infant bonding. Synthetic oxytocin during labor disrupts natural feedback loops, raising postpartum depression risks. Skin-to-skin contact post-birth restores natural secretion.
Leptin resistance fuels gestational weight retention
Placental leptin overproduction dulls maternal sensitivity to fullness signals. Postpartum leptin crashes prolong weight retention in 40% of mothers. High-protein diets improve leptin responsiveness and metabolic recovery.
The gut microbiome modulates hormonal interactions
Dysbiosis exacerbates insulin resistance and estrogen dominance. Probiotic strains like Lactobacillus rhamnosus lower gestational diabetes risk by 35%. Fermented foods improve hormonal clearance and reduce inflammation.
Autoimmune thyroid disease demands aggressive monitoring
TPO antibodies triple miscarriage risks even with normal TSH levels. Low-dose levothyroxine cuts preterm birth odds by 50% in antibody-positive mothers. Monthly thyroid panels prevent silent flares.
Preeclampsia roots in endothelial and hormonal cross-talk
Placental hormones like sFlt-1 damage blood vessels, spiking blood pressure. Low-dose aspirin begun before 16 weeks lowers incidence by 30% in high-risk women. Angiogenic markers predict onset earlier than blood pressure spikes.
Prolactinomas require delicate balancing during pregnancy
Benign pituitary tumors expand under estrogen’s influence, threatening vision. Dopamine agonists like cabergoline are paused due to fetal risks. Monthly visual field tests prevent permanent nerve damage.
Thyroid cancer surveillance continues through gestation
Well-differentiated cancers rarely metastasize during pregnancy. Ultrasound monitoring avoids radioactive scans. Surgery deferred to second trimester minimizes miscarriage risks. TSH suppression remains critical.
Endocrine disruptors lurk in everyday products
Phthalates in plastics lower testosterone, complicating fetal masculinization. BPA-free alternatives often contain equally harmful substitutes. Glass food containers reduce estrogenic chemical exposure by 90%.
Hyperemesis gravidarum signals thyroid or adrenal dysfunction
Severe nausea correlates with elevated hCG and TSH. IV hydration and thiamine prevent Wernicke’s encephalopathy. Ondansetron use requires cardiac monitoring due to QT prolongation risks.
Postpartum hormone crashes demand recognition
Plummeting estrogen and progesterone trigger depressive episodes in 15% of mothers. Transdermal estrogen patches alleviate symptoms within 72 hours for breastfeeding-compatible care.
Breastfeeding alters maternal endocrine recovery
Prolactin suppresses ovulation, delaying menstrual return. Weaning triggers estrogen rebounds and hair shedding. Gradual weaning smoothes hormonal transitions and reduces mastitis risk.
Thyroid antibodies breach the placental barrier
TPO antibodies cross into fetal circulation, raising autism spectrum risks threefold. Selenium supplements (200 mcg/day) lower antibody titers by 40% during pregnancy.
Cushing’s syndrome hides behind pregnancy weight gain
Dexamethasone suppression tests avoid false positives from placental CRH. Untreated cases cause 80% fetal loss rates. Midnight salivary cortisol tests differentiate pathology from normal rises.
Addison’s disease requires cortisol dose adjustments
Physiological cortisol demands triple by the third trimester. Undertreated cases risk fatal adrenal crises during labor. Hydrocortisone infusions prevent circulatory collapse during delivery.
Gestational trophoblastic disease mimics normal pregnancy
Elevated hCG levels spark false thyroid hyperfunction. Ultrasound distinguishes molar pregnancies from viable gestations by week 8. Methotrexate contraindications demand surgical evacuation.
Menopause symptoms rebound after childbirth
Estrogen withdrawal post-weaning mimics perimenopause in susceptible mothers. Black cohosh and acupuncture reduce hot flashes without affecting milk supply.
Polycystic ovaries remodel during pregnancy
Hyperandrogenism temporarily suppresses, restoring ovulation potential postpartum. Metformin continuation during breastfeeding maintains menstrual regularity in 60% of PCOS patients.
Thyroid storm threatens maternal and fetal survival
Heart rates above 140 bpm demand immediate beta-blockers. Propylthiouracil crosses the placenta less than methimazole. Delivery may be necessary to resolve refractory cases.
Insulin pumps offer precision in gestational diabetes
Continuous glucose monitors synced with pumps reduce hypoglycemia episodes by 70%. Postpartum insulin resistance drops within hours of placental delivery.
Hypoparathyroidism risks fetal skeletal demineralization
Calcium and vitamin D demands triple during lactation. Over-supplementation causes neonatal hypercalcemia. Twice-weekly blood tests balance maternal and infant needs.
Pheochromocytoma masquerades as preeclampsia
Paroxysmal hypertension and headaches demand plasma metanephrine testing. Delayed diagnosis carries 50% maternal mortality. Alpha-blockers stabilize blood pressure before surgical removal.
Growth hormone excess complicates acromegaly pregnancies
Tumor expansion risks visual field loss. Pegvisomant use lacks fetal safety data. Monthly MRIs monitor adenoma growth without radiation exposure.
Vitamin B12 deficiency mimics thyroid dysfunction
Fatigue and tingling hands signal low B12 in vegetarian mothers. Sublingual supplements bypass absorption issues caused by hormonal shifts.
Zinc deficiency amplifies gestational hypertension risks
Low zinc reduces placental antioxidant capacity, spiking preeclampsia odds. Oysters and pumpkin seeds restore levels without nausea triggers.
Melatonin regulates fetal circadian rhythms
Maternal melatonin crosses the placenta, programming sleep-wake cycles. Nightshift work disrupts secretion, raising preterm birth risks by 23%.
Iodine needs jump 50% during pregnancy
Severe deficiency causes cretinism and intellectual disabilities. Kelp supplements risk overshooting—150 mcg daily meets needs without thyroid overstimulation.
Maternal cortisol patterns shape infant temperament
High third-trimester cortisol correlates with colic and sleep disturbances. Mindfulness apps reduce maternal stress and infant fussiness by 35%.
Oxidative stress underlies placental aging
Vitamin C and E supplements reduce DNA damage in high-risk pregnancies. Overuse may paradoxically increase bleeding risks.
Placental lactogen drives gestational breast cancer risks
Elevated hPL levels activate oncogenic pathways in susceptible women. Postpartum MRI differentiates lactation changes from malignant masses.
Leptin surges correlate with postpartum depression
Placental leptin production plummets after delivery, destabilizing mood centers. Omega-3s and sunlight exposure restore leptin sensitivity gradually.
Pregestational diabetes demands preconception optimization
A1C below 6.5% slashes birth defect risks by 70%. Continuous glucose monitors started pre-pregnancy improve glycemic control.
Thyroid nodules require trimester-specific management
Fine-needle aspiration deferred until postpartum unless compressive symptoms arise. Levothyroxine suppresses growth in benign cases.
Prolactin inhibits maternal bone loss during lactation
Calcium drains into milk, but prolactin protects against osteoporosis. Weaning triggers rapid bone density recovery in most women.
Endometrial cancer risks linger after molar pregnancies
hCG monitoring continues weekly until undetectable, then monthly for a year. Early detection prevents malignant transformation.
Adrenal insufficiency complicates morning sickness management
Steroid doses must double during hyperemesis to prevent crisis. IV hydrocortisone prevents cardiovascular collapse in refractory vomiting.
